Subscribe to our blog
Thanks for subscribing to the blog.
January 31, 2015
Topics: Hybrid CloudAWS3 minute read
Here is some good news for our customers who are thinking about running Oracle workloads on NetApp Private Storage for Amazon Web Services (AWS).
NetApp Technical Report TR-4370 Oracle Performance on NetApp Private Storage for Amazon Web Services (AWS) is now available!
Here is the link: https://www.netapp.com/us/system/pdf-reader.aspx?m=tr-4370.pdf
For our NetApp field and partners, you can also find this Technical Report on the NetApp Field Portal.
For the TL:DR crowd:
- We compared Oracle performance on NetApp storage using local compute and Oracle performance using Amazon Web Services EC2 compute.
- The results of the testing showed that running Oracle workloads on NetApp Private Storage for AWS are comparable to running the same workloads using local compute.
- NetApp Private Storage for AWS a viable architecture for Oracle workloads
The Technical Report covers how the test environment was constructed and the testing methodology. What is great about how the testing was done is that we were able to come as close to an "apples to apples" comparison of the performance of Oracle using AWS EC2 compute and local compute running Cisco UCS C220 servers connected to the same NetApp storage via 10Gbps Ethernet network links.
We did this by placing the Oracle data and binaries on NFS exports on the NetApp storage (located in Equinix) and then mounting the NFS exports to the Cisco UCS C220 servers (located in Equinix) and then run the workload test using the SLOB2 utility. After the test run with the local compute was completed, we stopped Oracle, dismounted the NFS exports.
For the test run with the Amazon EC2 computer, we started up the AWS Ec2 compute and mounted the NFS exports on the NetApp storage (located in Equinix), started Oracle, and then ran the same workload test using the SLOB2 utility.
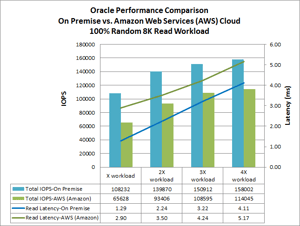
We gathered the performance data statistics from the NetApp storage and from Oracle to generate the following performance graphs. The first graph shows the test with 100% Random 8K Read Workload.
The performance curves show that the latency difference between on premise compute and the AWS EC2 compute is about 1-2ms. This makes sense as the network latency from our lab in Equinix and AWS is about 1-2ms.
The throughput isobars show as the workload increases the throughput also increases. As the workload reaches 4x, the throughput for both UCS and AWS EC2 begin to flatten out.
Overall, the latency and throughput track together as the workload increases.
The second graph shows the test with a 90% Random 8K and 10% Read workload.
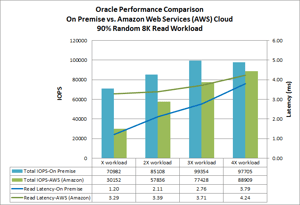
The performance curves are significantly different when we introduce write operations in the workload profile. At lower workload levels, the latencies different is greatest. The AWS EC2 performance curves remain relatively flat as the workload increases.
The performance curves for the Cisco UCS compute shows latencies being lowest at low workload levels and then approaches the same latency levels as AWS Ec2 compute at the higher workload levels.
The throughput isobars are very interesting as the AWS EC2 compute throughput increases as the workload increases. Although throughput is consistently higher for the local Cisco UCS compute, throughput for Cisco UCS compute peaks at 3x workload and starts to decrease at 4x workload levels.
Summary
Our testing results show that NetApp Private Storage for Amazon Web Services (AWS), delivers Oracle performance comparable to that of on-premises environments when running comparable workloads. NPS allows customers to benefit from the elasticity and economics of the cloud combined with the control, availability, and performance of NetApp storage.