More about NAS Backup
- Why Block-Level Backups Are 10 Times Faster and 1/10th of the Price of File-Level Backups
- Direct Backups: Why You Should Forget About Indirect Backups
- Cloud NAS Backup: Why and How to Move NAS Backup to the Cloud
- 5 NAS Backup Strategies and Their Pros and Cons
- NDMP: A Brief History, Architecture, and Common Topologies
- NDMP Backups Too Slow?: How to Shorten Your Backup Windows with Cloud Backup
- NAS Backup: Key Considerations for Enterprise Deployments
Subscribe to our blog
Thanks for subscribing to the blog.
November 10, 2022
Topics: Cloud Backup Storage EfficienciesFile ServicesBackup and ArchiveAdvanced10 minute read
Traditionally, backup has been time consuming and cost-heavy, even when updating incrementally. This situation has largely been due to the reliance on file-level based backups, mostly using the Network Data Management Protocol (NDMP). But block-level storage backups are changing that paradigm, making it possible to create backups in much less time and at a fraction of the cost of tape- and NDMP-based methods for NAS backup.
In this blog we’ll take a look at some of the problems with file-level backups, how block-level backups with NetApp Cloud Backup work, and why they’re faster and more cost effective.
Read on, or use the links below to jump down to the sections on:
- File-Level vs. Block-Level Backups
- What Makes File-Level Backups Inefficient?
- Block- Level Backups with Cloud Backup
- A File-Level Backup vs. Block- Level Backup Use Case
- It’s Time to Say Goodbye to File-Level Backups
File-Level vs. Block-Level Backups
For a technology that has been relied on for years, file-level back up methods—including those that rely on NDMP—suffer from extreme inefficiencies. These inefficiencies can cost you time and money.
For a technology that has been relied on for years, file-level back up methods—including those that rely on NDMP—suffer from extreme inefficiencies. These inefficiencies can cost you time and money. But first, let’s explain the difference between file-level and block-level backups.
What are file-level backups?
When we describe backups as “file-level” it means that they back up entire files and update entire files, even if only single data blocks within that file have changed since the previous backup was created.
What are block-level backups?
When we describe backups as being “block-level” what we mean is that these backups update only individual, changed data blocks as opposed to updating entire files. Snapshot technology is integral to creating these block-based backups.
Block-level backups are much more efficient than file-level backups.
What Makes File-Level Backups Inefficient?
What’s the reason behind file-level backup’s inefficiency? There are multiple factors involved.
Problem #1: File-Level Backups Back Up Too Much
The amount of data that needs to be copied and moved from the data source to the backup destination varies significantly depending on the type of backup.
- Full backups copy all the files in the volume
- File-level incremental backups copy files that have changed since they were last backed up
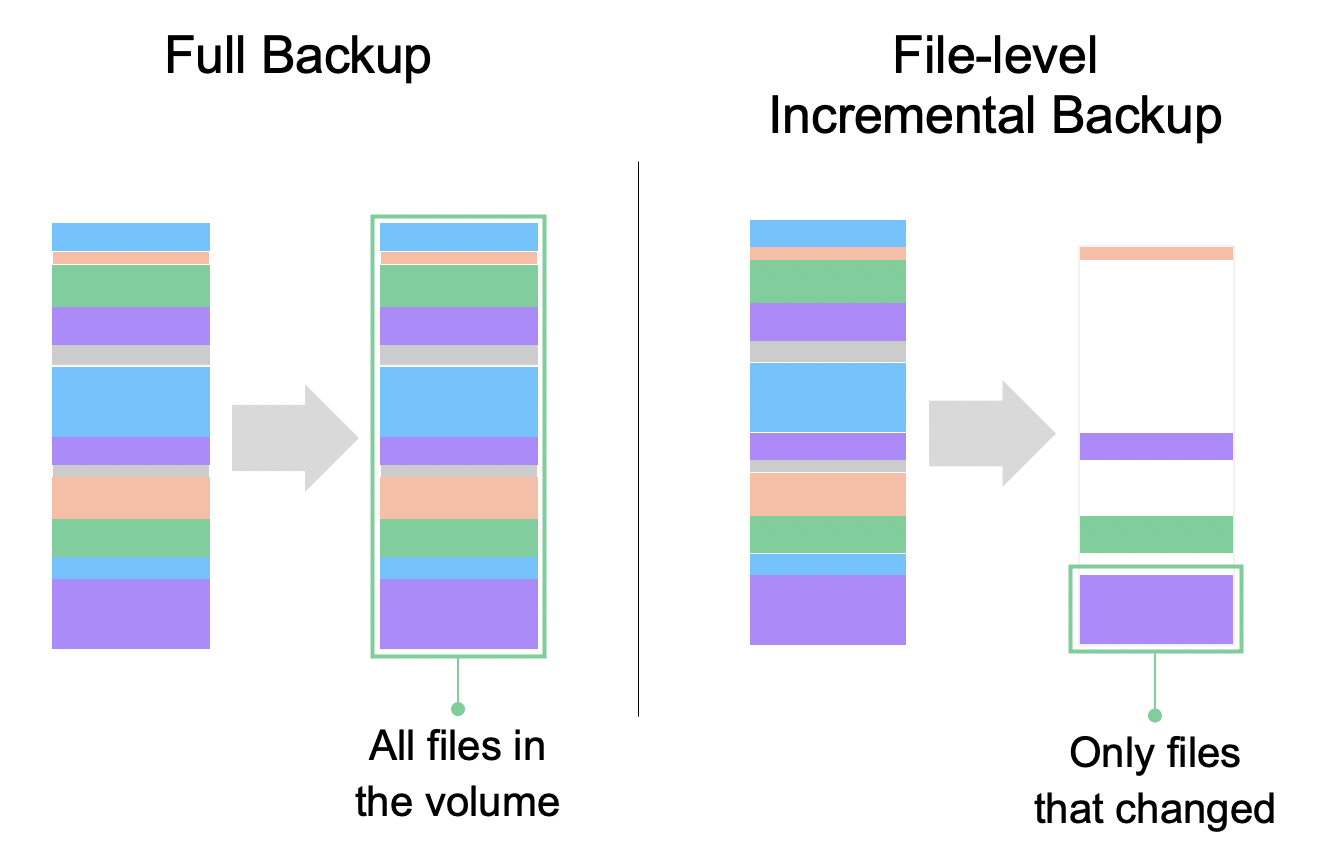
The issue with the file-level backup method is that copying over entire files will inevitably copy over more data than has been changed since the last backup has been created. For example, if a 1 TB file contains 3 KBs that have changed, the entire 1 TB file needs to be copied over.
Backing up entire files like this takes time and puts a lot of stress on the network. The more time it takes to create a backup, the more likely that changes to the live copy won’t make it over to the current backup. That means data loss, a red flag for effective backup systems.
Problem #2: Incremental File-Level Backups Aren’t Incremental Forever
Traditional NDMP-based backup solutions can only perform up to nine consecutive incremental backups. After that point, they need to create an entirely new full backup copy. That’s a time-consuming and costly task.
Typically, these systems are configured to perform five daily backups followed by a full backup over the weekend.
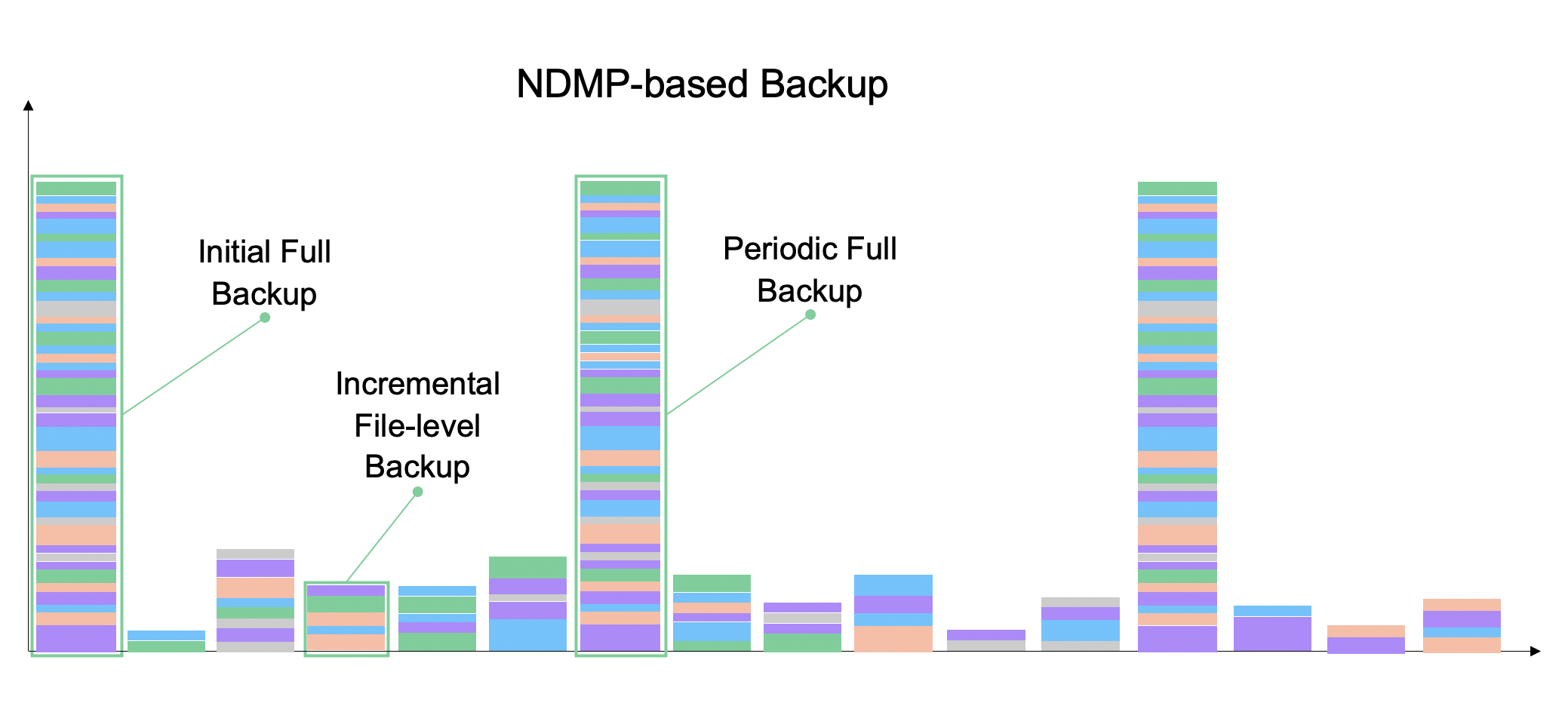
But for businesses that operate 24/7/365, the weekend may not offer the luxury to pause the system while that full backup is created. That means there will be some significant data loss between the primary and the copy.
Problem #3: File-Level Backups Don’t Back Up Directly
Since NDMP-based file-level backups can’t directly access the cloud, they leverage mediators to get the data from your ONTAP system to the storage repository.
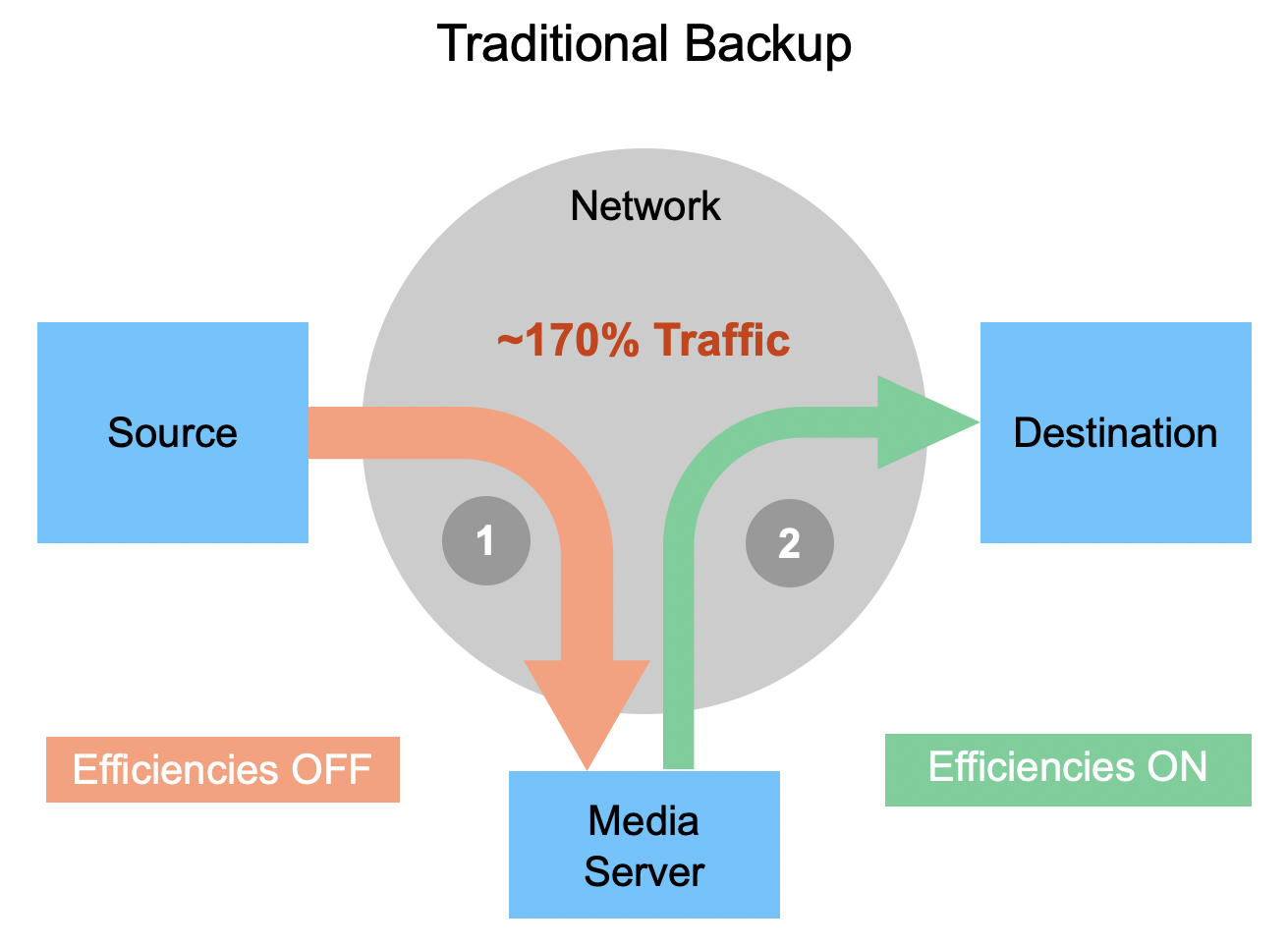
NDMP-based solutions first transfer data from the backup source to the media server in its raw format without storage efficiencies (deduplication and compression). Then it is moved from the media server to the backup destination.
There are a number of issues with the use of media gateways:
- The data is insecure. Since media gateways have to open files up as they move them between the source and destination, the data can’t be encrypted. That makes transferring through media gateways a major security concern.
- Storage efficiencies are lost. This time without the storage efficiencies. That means that your backup copy is now consuming more storage space than the primary data set. Restoring your data from such copies, if ever necessary, means that you will also need to recreate all of the efficiencies.
- Data is transferred twice. When backup copies are created your data has to make two jumps: once to the media gateway and once to the destination. This affects both the time it takes to safely back up systems and the stress put on your network.
- It is a single point of failure. If the media gateway fails, your entire backup and restore system goes with it. For enterprise-grade business continuity, that is simply not an acceptable risk.
- There is more hardware to maintain. Using a media gateway requires maintaining the entire infrastructure to support it. That means hosting dedicated hardware, with all the associated costs and overheads.
Block-Level Backups with Cloud Backup
Block-level backups solve the problems inherent with file-based backups, and NetApp offers them with NetApp Cloud Backup.
When ONTAP stores data, whether it’s in a file system or any other storage format, it organizes that data into chunks of 4 KB in size. These 4 KB aggregations are referred to as “blocks.” A single file can contain many 4 KB blocks. Note that these ONTAP blocks are unrelated to the “block” in the similarly named block storage technology.
Cloud Backup leverages ONTAP 4 KB data block structure and NetApp Snapshot™ technology to implement block-level backup for file storage which makes back up and restore operations more efficient and much faster.
Cloud Backup leverages object storage to create backup copies that are stored in object storage housed either in the cloud or in on-prem NetApp StorageGRID® appliances.
Cloud Backup’s block-level backups can simplify your ONTAP backup operations with more agility and more reliability:
- Backs up data at least 10 times faster than traditional solutions
- Consumes 97% less network bandwidth
- Takes 10 minutes or less to deploy
This high performance is possible thanks to a number of features that solve the problems that hamper file-level backups. Let’s take a look at them each in detail.
NetApp Cloud Backup is block-level.
Unlike file-level backups, Cloud Backup’s block-level incremental backup method only copies the data blocks that have changed after the initial copy is created.
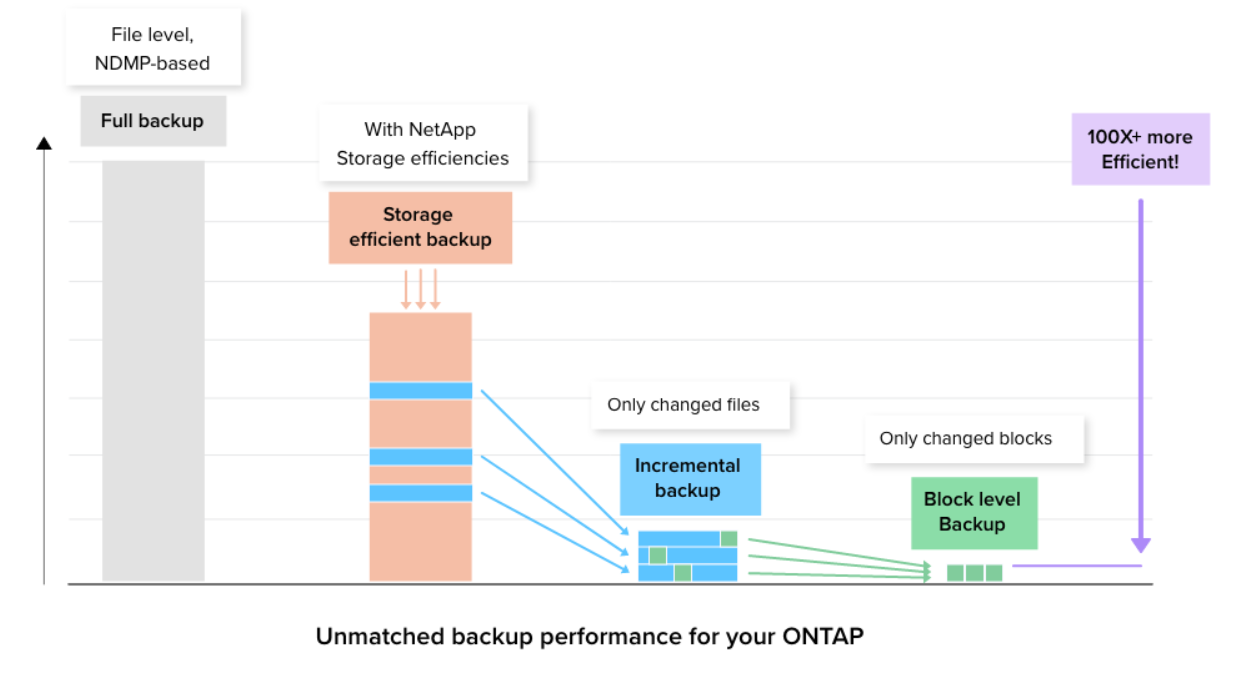
This provides several advantages over traditional NDMP-based backup solutions that perform file-level incremental backups.
- Less stress on production – It only sends blocks that have changed and not entire files removing unnecessary operations from storage and network resources.
- Less failures – File-level solutions can’t back up a file if it’s in use. Cloud Backup uses ONTAP SnapMirror® data replication, and it can access and back up data even if files are in use.
- Faster scanning – File-based solutions need to scan all the files to determine which ones need to be backed up. This is a time-consuming process, especially for large data sets. Cloud Backup uses lightning-fast and immutable NetApp Snapshot™ technology to instantly determine the changed blocks that need to be backed up.
- All data is backed up – Unlike NDMP-based file-level backups, Cloud Backup copies all the data, even if the files being backed up are open and in use. That means copies are complete and no data is lost.
- More secure – Cloud Backup also retains all of the ACL data with the copies, which ensures your data in the backup copy stays restricted to authorized users.
Cloud Backup is incremental forever.
Another unique advantage of using NetApp Cloud Backup is that after the one-time initial full backup is created, subsequent backups are incremental forever. This drastically minimizes the overall amount of data that needs to be transferred, contributing to its unmatched efficiency.
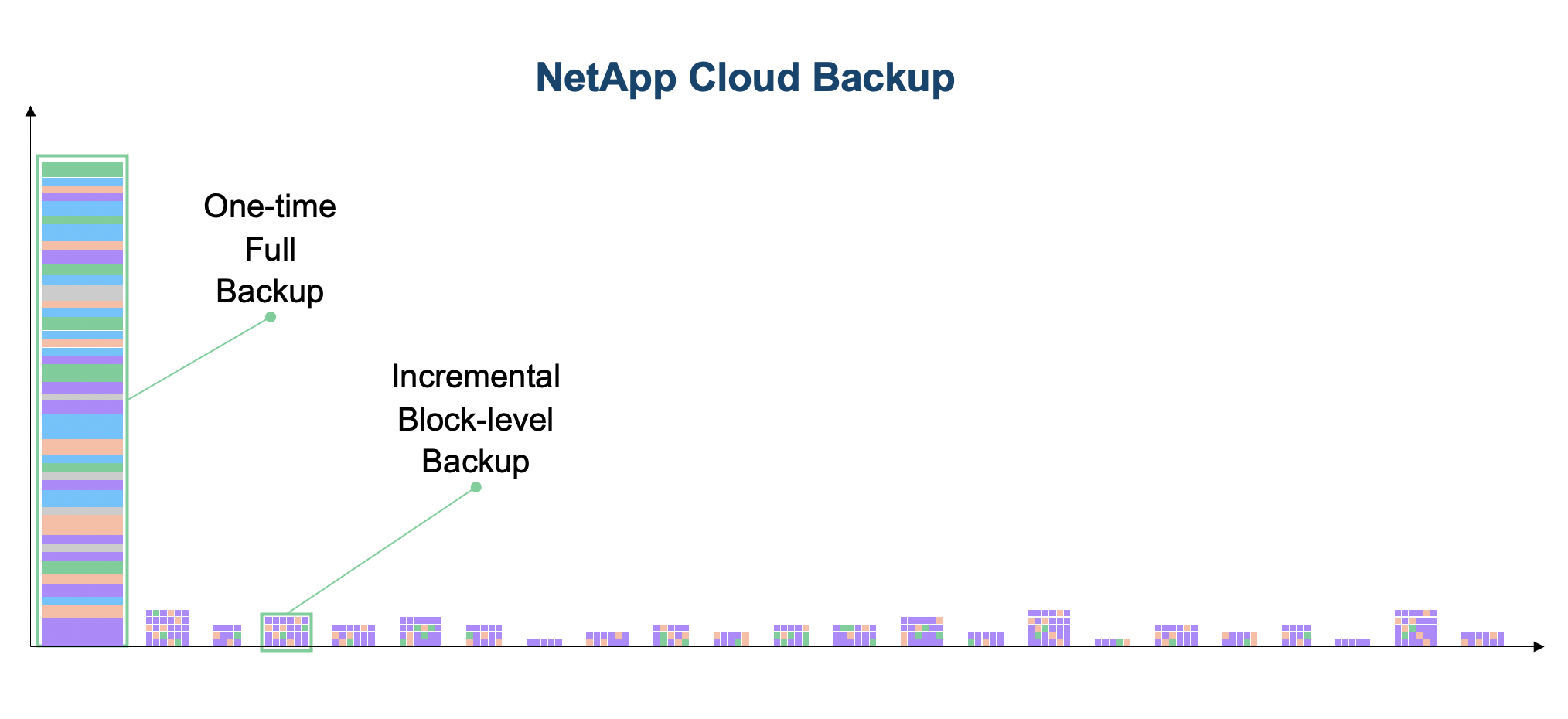
When there’s no need for periodic full backups, operations become much more efficient and there is less chance of missing a backup window.
Cloud Backup creates backups directly.
Another operational advantage is that Cloud Backup backs up and restores directly from source to destination while preserving ONTAP storage efficiencies end-to-end. This is not the case for traditional backup solutions which require a media server in between the source and destination.
NetApp Cloud Backup moves data directly from the ONTAP source to the object storage destination while preserving all of the existing ONTAP storage efficiencies.
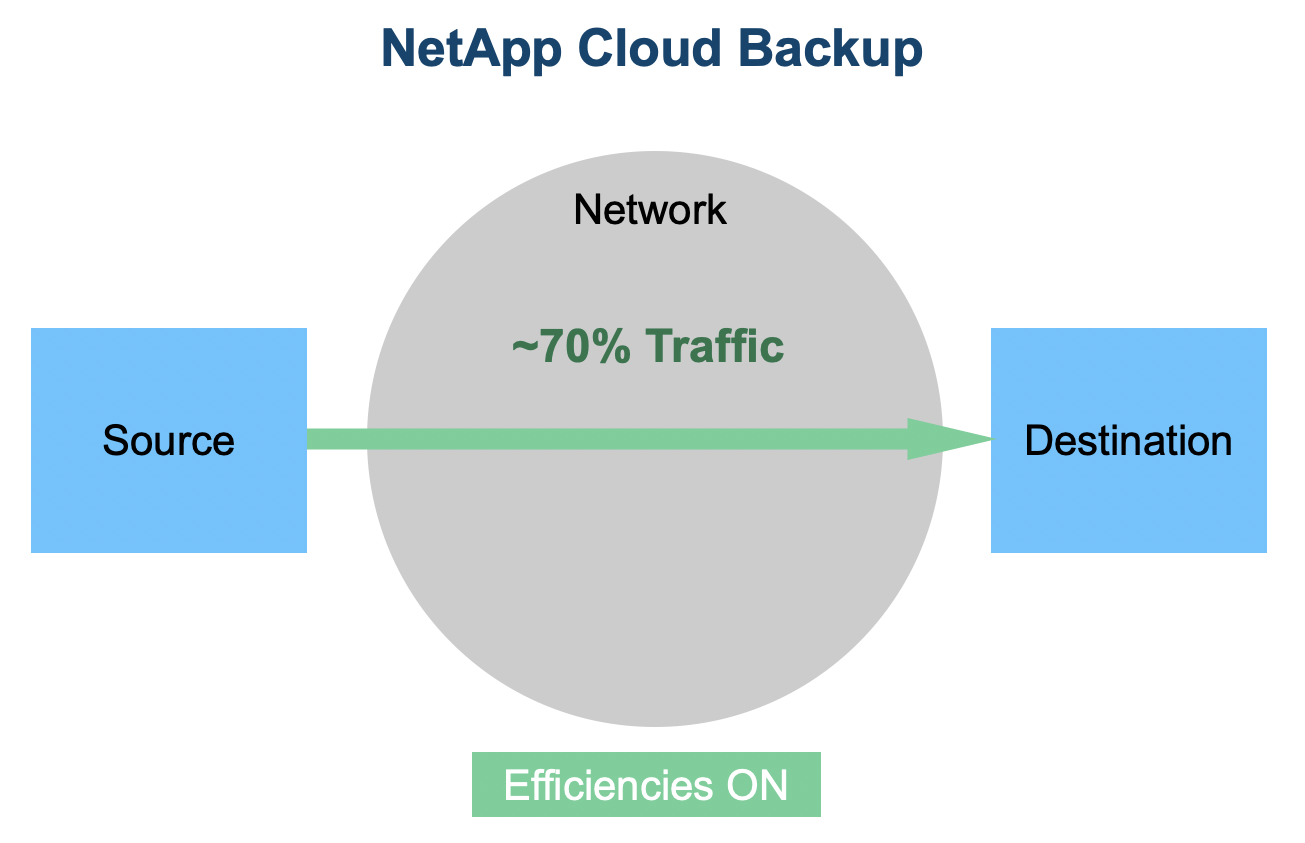
The advantages to directly backing up with Cloud Backup include:
- Less network traffic – By directly backing up from the source to the destination, Cloud Backup reduces network traffic to less than half the amount used by traditional solutions.
- Enhanced security – While media gateways open the files during the transfer process, they are not encrypted. Cloud Backup is more secure by keeping files encrypted end to end.
- No single point of failure – Since no media gateway is required, there isn’t a risk of a single point of failure in your backup system.
- Lower overhead costs – Directly backing up also removes the high overheads that come with careful sizing and operating additional infrastructure components.
Cloud Backup is a hybrid and multicloud solution.
Cloud Backup gives users more flexibility about how they deploy their backup storage architecture, offering a way to leverage either entirely cloud-based, entirely on-prem, or hybrid and multicloud solutions.
- Backup Source: ONTAP on-premises or Cloud Volumes ONTAP on AWS, Azure, or GCP
- Backup Destination: Amazon S3, Azure Blob, Google Cloud Storage, or NetApp StorageGRID
- Restore Destination: ONTAP on-premises or Cloud Volumes ONTAP (data can be restored to a location different from the source)
Cloud Backup is also available in all the regions available in these clouds.
This kind of flexibility is unmatched and simply not possible using NDMP-based backup solutions. For ONTAP users still looking to implement their first cloud service, Cloud Backup seamlessly integrates existing NetApp systems with pay-as-you-go object storage on AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud. Read more about what makes backup the perfect test workload for the cloud.
Cloud Backup can even be of use in the most restrictive environments, where absolutely all internet connectivity is prohibited, such as those required by certain governmental and military organizations. Using the software-only option of BlueXP, Cloud Backup can be deployed in a dark-site mode that does not require any internet access. All backups are stored efficiently in on-premises object storage using NetApp StorageGRID appliances.
A File-Level Backup vs. Block- Level Backup Use Case
To give you an idea of how all of the above advantages translate into operational efficiency, here’s a comparison of a traditional NDMP-based backup solution with Cloud Backup.
Let’s take 100TB of ONTAP NAS data that needs to be backed up daily. We’ll make some rough assumptions about this data set for simplicity:
- 5% of the files change per day (20% of the file data changes)
- Deduplication and compression reduce the data footprint by 30%
Using the file-level NDMP solution:
Over the weekend, there is a full backup, which moves 100 TB from the source to the media server and then 70 TB (deduped and compressed) from the media server to the destination. For the daily backups, the traditional NDMP solution moves 5 TB (5% of 100 TB) to the media server, and then 3.5 TB (5 TB with 30% deduped and compressed) to the backup destination.
The total backup traffic a week for traditional backup is (5 TB+3.5 TB) x 5 + 100 TB + 70 TB = 212.5 TB.
Using block-level Cloud Backup:
Once a day NetApp Cloud Backup moves 0.7 TB (20% of 5% of the 100 TB, with 30% deduped and compressed) from the ONTAP source to the backup destination.
The total traffic per week is 4.9 TB (0.7 TB x 7). In this scenario, Cloud Backup consumes 96.7% less network bandwidth than a traditional NDMP backup solution.
That level of efficiency means that data is backed up significantly faster with less risk of failure and less chance of network congestion that could interfere with production traffic.
It’s Time to Say Goodbye to File-Level Backups
As we’ve seen in this article, file-level backups can’t handle today’s demanding workload requirements. They simply can’t be created fast enough to ensure backup windows stay on target without data loss. Plus, file-level backups with the NDMP technology can’t leverage cloud storage and require media gateways that cost any of your existing storage efficiencies. The technology can’t keep up, and costs you more to maintain.
Block-based backups offer a superior experience, one that doesn’t risk losing data during backup operations. backups can fully leverage.
Cloud Backup gives users an easy way to create block storage backups on object storage service of your choice of public cloud or on a StorageGRID appliance on-prem. Besides the benefits of backing up data at the block level, Cloud Backup offers a number of additional benefits:
- Indexed catalog
- Archive tiers support
- DataLock
- Ransomware Protection
- Single file restore
- Application-consistent backups
These various parts all come together to make Cloud Backup a faster and more secure enterprise-grade solution for backup and restore.
