More about Google Cloud Backup
- Google Cloud Disaster Recovery and Data Protection with Cloud Volumes ONTAP
- Google Cloud Storage Retention Policy: A How-To Guide
- Google Cloud Automatic Backup: How to Use Schedules to Back Up Persistent Disks
- Google Cloud Compute Engine Snapshots: A How-To Guide
- Google Cloud Snapshot: Data Backup and Restoration
- Google Cloud Backup: Making the Most of Google’s Storage Tiers
Subscribe to our blog
Thanks for subscribing to the blog.
November 2, 2021
Topics: Cloud Volumes ONTAP Data ProtectionGoogle CloudDisaster RecoveryAdvanced9 minute read
The tools and processes an organization has at its disposal to ensure data protection with Google Cloud increase significantly compared with the ones available in traditional on-premises data centers. But there are still challenges to consider, namely data protection, which includes your Google Cloud disaster recovery and Google Cloud backup plans.
With more government regulation and compliance requirements appearing in recent years, combined with an increased demand for globally available systems and infrastructure, it is safe to say that both the expectation level and challenges an organization faces to ensure data protection and privacy have also grown.
In this post we’ll take a closer look at the data protection challenges Google Cloud users face, disaster recovery capabilities provided by the Google Cloud platform, and how Cloud Volumes ONTAP can provide improved data protection.
In this article:
- Data Protection Challenges
- Google Cloud Disaster Recovery: Key Components
- Setting Google Cloud Disaster Recovery: 3 Common Scenarios
- Adding Value with Cloud Volumes ONTAP Data Protection Capabilities
- A Better Solution for Data Protection Challenges
Data Protection Challenges
It can be a daunting task to get a holistic view of what an organization needs and can use for Google Cloud data protection. This can be challenging at any time, but possibly even more so when juggling the many tasks involved with a Google Cloud migration.
While cloud managed services act as solid building blocks that can make this less painful, with features such as storage snapshot technology and multi-region replication, it still requires deep tech expertise to design and orchestrate a highly available system that can properly implement Google Cloud disaster recovery, backup data protection, and security measures. Bottom line: as engineers, we know that it will require a significant amount of effort (time and money), and it can be really challenging to tick all these boxes.
However, the true challenge of data protection goes beyond mere technical capabilities. The biggest challenge is what and how an organization can govern the data they store and process. Today, security and compliance are critical areas for businesses running on Google Cloud. GDPR, CCPA, PCI-DSS, and other regulatory guidelines can help, but it is ultimately the responsibility of the organization to handle the data subject requests, audits, and overall making sure everything is properly taken care of.
Therefore, from a business point of view, you want to minimize the risk of a service disruption, data breach, and corruption, all of which can expose your organization to a potential loss of revenue and business impacts due to operational disruption, reputation damage, lawsuits, and compliance issues.
Google Cloud Disaster Recovery: Key Components
Google doesn’t offer any products specifically intended for disaster recovery, but it does offer guidance for teams building a cloud DR system. Google Cloud provides several products and features that are useful as building blocks for DR architectures.
Compute Engine
Compute Engine is the driver of Google Cloud, providing virtual machine (VM) instances, as well as a number of features you can leverage for your DR plan. For example, you can set the delete protection flag to prevent the accidental deletion of VM instances.
Cloud Storage
You can use Google Cloud Storage to store objects like backup files in various storage classes. For DR, you can leverage lower-cost classes like Nearline storage (as well as Coldline and Archive) to save on storage costs while enabling periodic DR stress testing. Note that retrieving data can incur extra costs.
Filestore
A Google Cloud Filestore instance is a fully-managed network file system (NFS) server for applications that run on Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) clusters or Compute Engine instances. This is helpful for disaster recovery, as applications can switch to Filestore in a failover region to restore Filestore volume access before a restore process is completed.
Cloud Load Balancing
Cloud Load Balancing distributes requests across multiple instances to provide Compute Engine high availability. It can be configured with instance health checks to prevent traffic from being routed to failing instances.
Traffic Director
This service mesh traffic control plane can handle the configuration of proxies running in GKE and Compute Engine. You can make a service highly available by deploying it in multiple regions. Traffic Director initiates failover proxy configuration to redirect traffic from unhealthy instances.
Cloud DNS
Cloud DNS allows you to programmatically manage DNS entries in an automated recovery process. Cloud DNS uses redundant locations globally via an Anycast name server network for low latency and high availability.
Cloud Monitoring
Cloud Monitoring tracks events and metrics (with metadata) from Google Cloud and various application components. With the proper configurations, it can send alerts to third-party apps and tools that trigger automated DR processes in response to the alerts.
Deployment Manager
Deployment Manager provides templates for defining Google Cloud environments. The templates allow you to easily create or dismantle your environment with a simple command.
Additional Disaster Recovery Features
Google Cloud offers a number of additional features that are useful for planning your DR, including:
- Global network—Google’s network is among the largest and most advanced in the world. It leverages advanced networking software and edge caches to provide fast, consistent performance.
- Redundancy—Google’s global network comprises numerous points of presence (PoPs), ensuring that data is automatically mirrored across multiple storage devices in different locations around the globe.
- Scalability—as with other Google products, Google Cloud supports fast scaling capabilities to help you handle spikes in traffic. You can leverage managed services like Datastore, App Engine and Compute Engine Autoscalers to automatically scale applications up or down.
- Security—Google has a mature security model that helps keep users safe on applications such as Workspace and Gmail. Google also has site reliability teams that help maintain high availability and prevent the resources of the platform from being abused..
- Compliance—Google regularly undergoes independent, third-party audits to ensure that services like Google Cloud are compliant with privacy and security regulations. These include SOC 2/3, ISO 27001 and PCI DSS 3.0 certifications.
Setting Google Cloud Disaster Recovery: 3 Common Scenarios
1. On-Premises Production Environment
There are several ways you can leverage Google Cloud to back up your data if you have an on-prem production environment, with the cloud serving as a recovery site. The following are two potential solutions.
Storage Transfer Service
You can back up on-premises data to Cloud Storage with Transfer Service. This is useful given the complexity of transferring large volumes of data across networks and the associated risk of data loss. This managed service is reliable and scalable, allowing you to transfer data from a data center to Cloud Storage buckets.
Partner Gateway Solution
You can use a partner gateway solution to back up your data to Cloud Storage. Integrated third-party backup and recovery solutions can apply tiered storage strategies to prioritize recent backups while saving costs on older backups (for instance by using slower storage tiers like Archive). Backup data can be recovered in the event of a failure, with a DR environment serving production traffic while the production environment is being restored.
A partner gateway facilitates the transfer of data from on-premises to cloud storage, as illustrated in the following diagram.
Image Source: Google Cloud
2. Google Cloud Production Environment
If both your production and disaster recovery environments run in Google Cloud, you can leverage storage tiering for data backups. You can migrate backup data to cheaper storage tiers, because the likelihood of accessing it is lower. Nearline, Coldline and Archive are useful for storing infrequently used data, but they require minimum storage durations and have additional costs for retrieving data.
The storage tiers for a production workload in Google Cloud are illustrated in the following diagram.
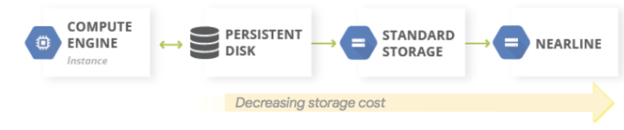 Image Source: Google Cloud
Image Source: Google Cloud
3. Production Environment in a Different Cloud
If your production environment runs in another cloud, you can still use Google Cloud as a recovery site for your disaster recovery plan. It is common for DR strategies to involve transferring data from one object store to another.
You can use Storage Transfer Service to transfer data to Google Cloud from Amazon S3. You can configure transfer jobs to periodically synchronize the data source and data sink, and apply filters (i.e. by file name or creation date) to control how and when data is transferred.
You can use the Boto Python tool to transfer data to Google Cloud Storage from AWS. You can install it as a plugin via the gsutil command-line tool.
Adding Value with Cloud Volumes ONTAP Data Protection Capabilities
NetApp Cloud Volumes ONTAP is an innovative data management solution for Google Cloud that enhances the existing Google Cloud services. It provides out-of-the-box storage capabilities, such as data protection, storage efficiency, cloning, tiering, storage hybridity and much more. Cloud Volumes ONTAP features are especially useful for organizations with demanding data governance needs.
Cloud data protection is a key element of a good cloud strategy and governance. NetApp Cloud Volumes ONTAP covers the different data protection challenges an organization faces, and overall simplifies the storage management.
NetApp Snapshot Copies
The ability to create point-in-time copies of a storage volume is crucial for data management. The snapshot functionality that exists in most cloud storage services provides that ability, enabling incremental copies of your data and serving as a means of backup. There are however, key aspects that differentiate how different storage services implement this technology.
Contrary to the Google Cloud own storage services, NetApp Snapshot™ technology does not require a full copy of the source data, which allows snapshots to be taken and restored much faster. A traditional limitation of snapshots is that to ensure a complete and consistent copy of the data, the compute instances should suspend data writes during the snapshot creation process. NetApp Snapshot copies are created instantly, and users can keep up to 255 snapshots of a hot, active file system without any performance degradation.
In addition to the performance and flexibility, the NetApp Snapshot copies also end up saving you money due to the space optimization compared with other snapshot technologies, enabling snapshots to be automatically transitioned to inexpensive storage tiers.
Backup and Recovery
Data protection strategy is not complete without a proper process and mechanism for backup and recovery. While using Google Cloud, as per the cloud shared responsibility model, the customer is ultimately responsible for the deployed resources, which includes making sure backup data protection is in place. It is also essential to consider not only the data you store in Google Cloud, but also any other data storage locations such as on-premises or additional cloud providers.
It is important to have a well-defined process and service that can store data safely and securely throughout its entire lifecycle. In addition to the usage of a snapshot technology, it is crucial to have data archives that can be used to store data that is still valuable to the organization but might not be in active use anymore.
NetApp Cloud Volumes ONTAP enables data replication—that acts on the current state (version) of the data volume—and data archiving capabilities, which provide a way for organizations to backup data volume historical versions, for audit purposes, saving costs, or meeting compliance requirements. This feature enables organizations to backup data in an efficient way and without Google Cloud data storage costs getting out of hand.
Furthermore, because Cloud Volumes ONTAP work across multiple cloud providers and on-premises locations, it makes it simpler to implement a backup and recovery process and have a holistic data protection strategy.
Google Cloud Disaster Recovery
Often, backup and disaster recovery are confused because they both share a similar logic and goals, yet there are significant differences between them. A backup is designed to help recovering from data corruption and service disruptions in a given infrastructure environment, while disaster recovery is slightly different and expands this ambition behind this goal.
The main objective of disaster recovery remains the same as backups, in that it enables the organization to recover data in case something happens—but disaster recovery goes beyond this goal and has often different service level agreements, infrastructure location, and data integrity requirements. Disaster recovery is designed to help recover the whole infrastructure, making it possible to seamlessly failover the entire operation to a secondary copy during a disaster and then failback when the problem has been resolved, even in a different location if required.
NetApp Cloud Volumes ONTAP DR provides a significant advantage compared with Google Cloud built-in storage services. Because Cloud Volumes can be easily made available in different locations, it makes it extremely easy to create a remote replica of your environment in a different location and have it ready to take over in case of a failure in the primary environment.
Using SnapMirror®, Cloud Volumes ONTAP’s built-in replication technology, the entire Google Cloud disaster recovery process can be offloaded from custom business logic running on instances to the built-in capabilities of the storage solution itself, thus ensuring a fully-synchronized mirror site of the environment. In addition, it comes with out-of-the-box support to make this possible across different availability zones, regions, or even cloud providers, ensuring that organizations have maximum flexibility regarding the location of their secondary replica environment.
This entire DR process is cost effective, as Cloud Volumes ONTAP’s storage efficiencies make the secondary copy even less expensive to store in the cloud. Besides deduplication, compression, and compaction, Cloud Volumes ONTAP also allows the entire copy to be tiered to inexpensive Google Cloud Storage, where costs are much lower than on Google Performant Disk. When the copy is needed, Cloud Volumes ONTAP shifts it seamlessly back to Performant Disk for rapid use.
Data Security
The security of an organization's data is vital to its day-to-day operations. A data breach or corruption can ruin the reputation and cause massive revenue loss. The storage service needs to support encryption at rest as well as in transit, and enable strict data access control. As we mentioned earlier, Google Cloud KMS and IAM help to address these requirements. However, data security in an enterprise environment expects additional capabilities from a storage service itself.
A growing concern for enterprise organizations is handling data security in multi-tenant cloud environments. Since the underlying resources are sometimes shared by multiple departments, business units, or external customers, it is important that an organization can take precautions against any kind of unauthorized access.
Cloud Volumes ONTAP’s data security features build on this, enabling organizations to use different encryption technologies both at rest and in transit using the SMB3+/NFS4.1+ protocols and immutable write-once/read-many (WORM) storage volumes. In addition, Cloud Volumes ONTAP comes with out-of-the-box Vscan antivirus integration and ransomware protection, ensuring both the integrity, availability and reputation of your organization.
High Availability
The Cloud Volumes ONTAP high availability (HA) configuration for Google Cloud changes the game in terms of how organizations can achieve high availability. It meets the highest service level agreement and guarantees an RPO (recovery point objective) of 0 and RTO (recovery time objective) of less than 60 seconds, while ensuring strict compliance and data integrity requirements.
Traditionally fulfilling these requirements and expectations with on-premises data centers has been a highly challenging endeavor. With cloud, managed services make it possible to create highly available systems with less hassle, however choosing the right services and configuration combination of such a solution still requires expert knowledge.
NetApp’s Cloud Volumes ONTAP dual instance HA configuration provides a ready-made solution for storage in the cloud without the risk of data loss. With HA enabled, all data volumes can be synchronously mirrored across multiple locations, with operations only completing after all the information has been written to each Cloud Volumes ONTAP node. This allows different high availability scenarios and modes of operation such as active-active, where data can be written to either node, or active-passive, where one of the nodes stays in standby and only serves out reads.
A Better Solution for Data Protection Challenges
As we saw throughout this article, Google Cloud disaster recovery and data protection can be enhanced by NetApp Cloud Volumes ONTAP’s capabilities to enable more secure cloud deployments. Moreover, it will optimize the cloud storage costs and performance, by using built-in storage efficiency capabilities and automatic storage tiering, shifting infrequently-used data to the appropriate storage type without manual intervention.

